Your AC capacitor is a small but important part hidden behind your AC’s housing. If it breaks, you might hear a humming sound, and your unit could start blowing warm air instead of cool.
Even worse, a bad capacitor of AC can also make your energy bills higher because your system isn’t working efficiently.
That’s why it’s good to know how to test it and when to call in air conditioning services. So, let’s dive in!
What is an AC Capacitor?
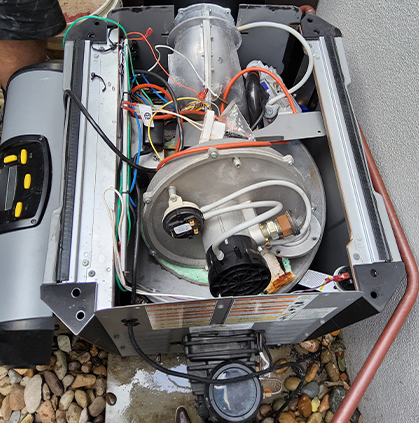
An AC capacitor is typically a metal cylinder that you’ll see inside your outdoor AC unit. It’s attached to a bracket near the compressor or connected to the metal housing.
It has two to four wires coming out from the top that connect to your compressor and fan motors. Most homeowners won’t deal with these AC unit parts, unless they need to be replaced.
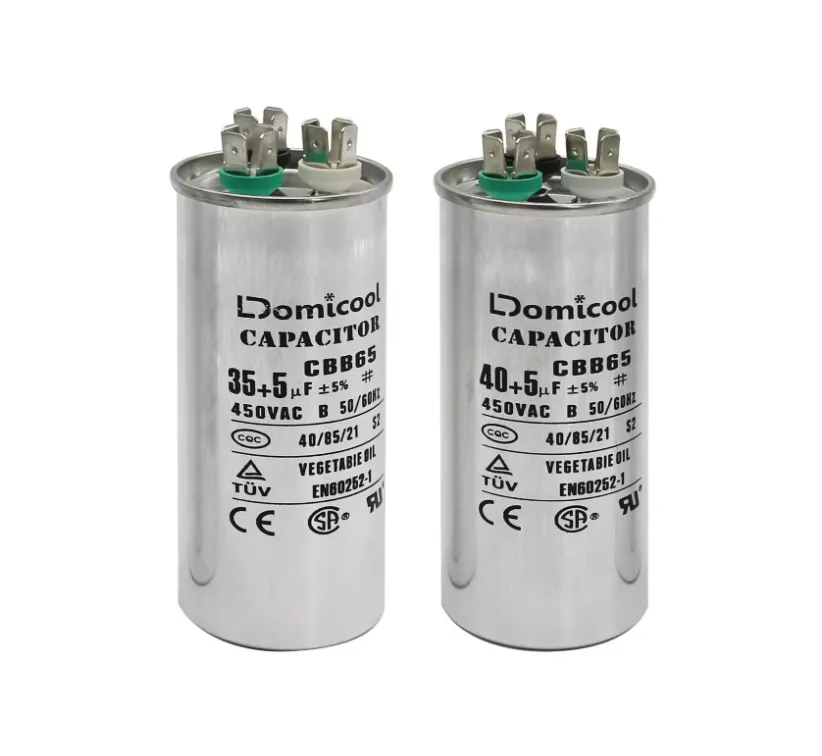
So, what does a capacitor do in an HVAC system? As its name suggests, an AC capacitor stores electrical energy. It has a number on its label that shows how much energy it can store, measured in microfarads (µF).
You’ll see numbers like “35+5” or “70/7.5”. The first number handles the compressor boost, while the second supports the fan. You’ll also see a letter like “C” or “R” indicating the capacitor type or manufacturer.
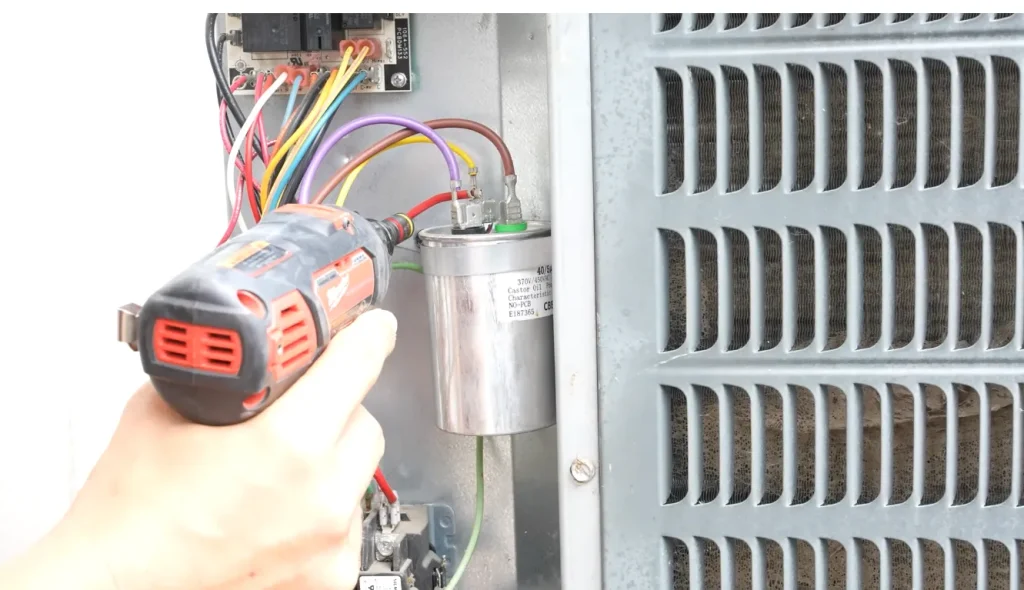
Sometimes, you’ll see a letter like “C” or “R” on the label, which shows the type of capacitor or manufacturer.
It also shows the voltage rating (370V or 440V) and tolerance (±5% or ±6%),
But an AC capacitor actually does more than being a battery. It also releases energy quickly when needed. Think of it like a caffeine shot for your system. It helps motors like the compressor start and keeps them running.
If it fails, your AC might not turn on at all, keep shutting off randomly, or your AC not blowing cold air.
How Does an AC Capacitor Work?
A capacitor, in general, stores electrical energy when you apply voltage. It charges up slowly, creating an electric field. And when there’s a sudden need for power, it quickly releases that stored energy.
Now, how does a capacitor for an AC unit really work in both ducted system and split systems installation?
- Power is supplied to the AC system — When you turn on the AC, electricity from your home’s main power flows through the wires to the unit. That’s when the capacitor gets ready to do its job.
- Capacitor charges up with electrical energy — The capacitor starts charging when the current flows in. It gradually stores energy as an electric field, creating a reserve to use later.
- The motor needs extra power to start or run — When the motor needs more power, that’s exactly when the capacitor jumps in. Its stored energy gives your motor the help it needs to get the job done.
- Capacitor releases stored energy to the motor — Right when your motor needs a power boost, the capacitor instantly releases all its stored energy. This gives the motor that extra kick it needs to start up.
- The motor starts smoothly or continues running — With that energy boost from the capacitor, your motor starts smoothly and runs steadily. This helps your entire AC unit work more efficiently.
- Capacitor recharges for next use — After it releases its energy, the capacitor sits empty until the power flows again, recharging it for the next time your motor needs a boost.
Types of AC Capacitor
There are more than eight AC capacitor types, but for homeowners three core ones matter most:
1. Start Capacitors
A start capacitor is an AC capacitor that provides your HVAC system’s compressor or blower fan with the extra push needed to start. They generally have larger capacitance values compared to run and dual capacitors.

It sends a quick burst of electrical energy, called inrush current, to start things, especially under heavy load. A relay keeps it engaged briefly and then turns off once it’s running.
These capacitors have high microfarad ratings, usually between 50–1200 µF, with 88–108 µF being a common range.
2. Run Capacitors
A run capacitor is a type of AC capacitor that helps the compressor and fan motors run smoothly. It activates after the start capacitor cuts and stays in the circuit to maintain motor operation.

It works by shifting the electrical current, which lets the motor keep a steady speed and actually use less energy.
3. Dual Capacitors
A dual capacitor is like a 2-in-1 unit. It combines the jobs of both a start and a run capacitor into a single, compact part. This simpler design is also cheaper.

It gives that powerful jolt to get the motors spinning and then sticks around to keep them running smoothly and efficiently. It’s responsible for the whole life of the motor’s operation.
Dual capacitors have higher microfarad (µF) ratings. A common one might be 35-80 µF for the compressor and 5-10 µF for the fan side.
How to Test an AC Capacitor?
A bad capacitor can cause your AC to break down or lose efficiency. You can test your capacitor for AC if you’re careful to help your AC run better and last longer. But how to do it?
WARNING: You should know how AC system works before doing this and never try to replace an AC capacitor yourself.
1. Turn Off the Power
Go to your home’s circuit breaker and turn off the power to your outdoor AC unit. This safety step prevents electric shock. Make sure the unit is truly off before touching anything inside.
2. Find the Capacitor
You can then take off the metal cover on your outdoor AC unit with a screwdriver. After it’s removed, find the small, round part. That’s your capacitor with wires connected to the top of it.
3. Do a Visual Inspection
You need to do a visual inspection when checking your AC capacitor. Look for warning signs like the top or sides bulging out, oily liquid leaking from the bottom, or visible cracks or burn marks.
If you see any of these, the capacitor is probably broken and needs to be replaced.
4. Safely Discharge the Capacitor

An AC capacitor can give a dangerous shock even when off. So, the next step is to use a discharge tool with a bleeder resistor.
For lower-voltage units, an insulated screwdriver can carefully connect the terminals to release the energy.
5. Mark and Unplug Wires
To avoid forgetting wire connections, mark each with its terminal, like “C” for Common, “FAN” for the fan, and “HERM” for the compressor. This simple step makes sure you’ll hook everything back up correctly.
6. Set Your Multimeter to Capacitance Mode
To test the AC capacitor, you’ll need a digital multimeter. Set it to the capacitance setting. That’s the best way to get an accurate reading.
If your meter doesn’t have that, you can use the resistance or voltage settings, but they’re not as precise.
7. Test Your AC Capacitor
You can touch the multimeter’s probes to the capacitor’s terminals. For a dual capacitor, place the red lead on the “C” (common) terminal and the black lead on either the “FAN” or “HERM” terminal.
Make sure you have a solid connection, or your reading won’t be accurate.
8. Reading the Value
Check your multimeter reading and compare it to the capacitor’s μF rating. A good capacitor will be within the specified tolerance (like ±5% or ±10%).
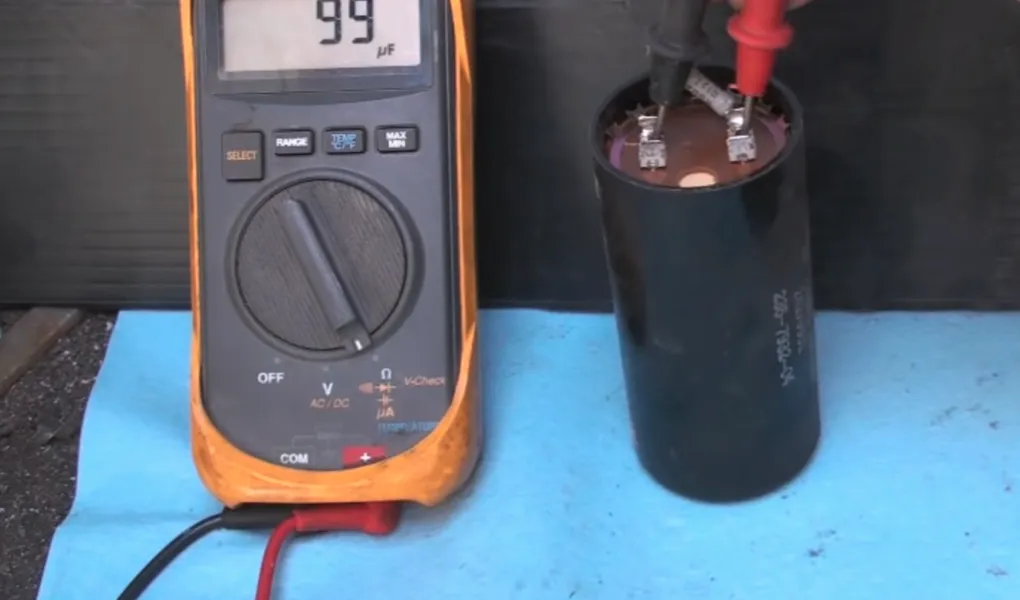

If the reading is much lower or shows no reading, the capacitor has likely failed and needs replacing.
When Should You Replace Your AC Capacitor?
If you see these symptoms, that’s the time to replace your AC capacitor:
- The AC won’t start because a bad capacitor can’t boost the motor.
- Warm air coming out of the vents
- You hear strange humming or buzzing noises outside, but your AC isn’t cooling.
- Your AC keeps short cycling, affecting your home’s cooling.
- Your AC system takes longer than usual to start
- You smell burning from your AC. It could be due to electrical problems, or overheated parts like capacitor
- You have higher energy bills because your AC works harder and uses more electricity
- If the circuit breaker trips every time you turn on the AC
FAQ about AC Capacitor
These are some questions that could come up when you want to learn about AC capacitors and how they work:
Can an AC run without a capacitor?
No, an AC cannot run properly without a capacitor. It is needed to start the compressor and fan motor, and it helps your system run smoothly.
What happens when an AC capacitor fails?
When the capacitor fails, your AC might not start, run inefficiently, or not cool properly. You could also hear strange noises or see it shut off frequently.
What is the most common reason for capacitor failure?
The common reason capacitors fail is because they overheat, usually from power surges, or due to wear and tear over time.
How much does it cost to replace a capacitor in an AC unit?
Most homeowners pay between AUD 150 and 350 for parts and labour. However, if you require a dual-run model or need after-hours service, it will cost more.
Can I replace an AC capacitor myself?
Yes, you can replace an AC capacitor yourself. But, it is not recommended due to the risk of electrical shock. It is safer to have a professional handle the replacement.
Conclusion
Now that you know how a bad AC capacitor can cause issues, you can keep testing and taking care of your AC.
But, even if you can do it yourself, it’s better to call a professional to replace it. Our trained technician at Lightning Bult will do the job safely and correctly, making sure your AC works well and keeps you comfortable.